The Pregnancy Mortality Surveillance System (PMSS) is a national surveillance system tracking pregnancy-related deaths, or deaths that occur during pregnancy and up to one year after. It is used to measure the pregnancy-related mortality ratio (deaths during pregnancy and up to one year after per 100,000 live births).
PMSS collects data from death certificates, medical records, and other sources to help identify trends, causes, and risk factors for pregnancy-related mortality.
Pregnancy Mortality Surveillance System
Where does the data come from?
The CDC requests data from all 50 states, Puerto Rico, the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, New York City, and Washington, DC. These reporting areas voluntarily submit data for all women ages 10-60 years old who died during or within 1 year of the end of their pregnancy, regardless of the cause of death (aka all pregnancy-associated deaths). If a death is linked to a live birth or fetal death, those records may also be shared.
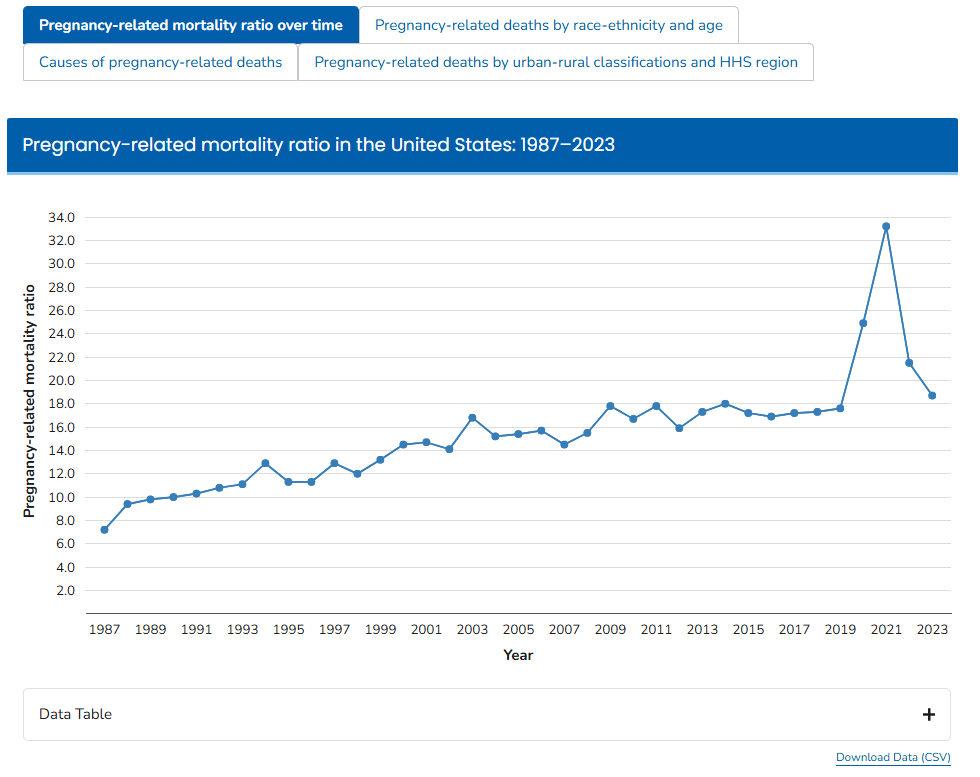
Explore the dashboard
In 2025, after completing the analysis of 2023 PMSS data, the CDC launched a new dashboard that allows users to view data trends over time and toggle between different years to see the leading causes of pregnancy-related deaths that year, as well as pregnancy-related deaths by race-ethnicity, age, urban-rural classification, and HHS region.
Key PMSS Definitions
PMSS disaggregates data based on various factors. This is how the CDC defines these factors:
-
Race and ethnicity information is based on the linked birth or fetal death records, when available, and from death records when a birth record or fetal death record was unavailable. Race and Hispanic origin are reported separately on the birth, fetal, and death records; more than one race can be selected. All deaths with a notation of Hispanic origin are classified as Hispanic, regardless of race. For deaths with missing notation of Hispanic origin, race, or both, the decedent's race-ethnicity was classified as unknown. Among non-Hispanic women, those that select a single race are classified as: non-Hispanic White, non-Hispanic Black, non-Hispanic American Indian or Alaska Native (AI/AN), non-Hispanic Asian, non-Hispanic Native Hawaiian or Other Pacific Islander (NHOPI). Among non-Hispanic women, those that select a multiple race categories are classified as non-Hispanic Multiple Race.
-
We use age information from the death record.
-
Urban-rural classifications are defined by the Urban-Rural Classification Scheme for Counties. Metropolitan counties, such as large central, large fringe, medium, and small, can be considered urban. Micropolitan and noncore counties can be considered rural.
Urban-rural classifications are based on county of last residence from the death record, when available, and from the birth or fetal death record when missing or undetermined on the death record. Federal Information Processing Series (FIPS) codes were applied to each record using the resident state and county FIPS codes provided on the record by matching the decedent's resident county and/or ZIP code to its corresponding county FIPS code using the Housing and Urban Development (HUD)-United States Postal Service (USPS) ZIP Code Crosswalk and the United States 2020 Census County Name FIPS table.
-
HHS regions, defined by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services as of January 2025, are based on residence at the time of death when available, and from the birth or fetal death record when missing or undetermined on the death record.